Greater loss and fragmentation of savannas than forests over the last three decades in Yunnan Province, China
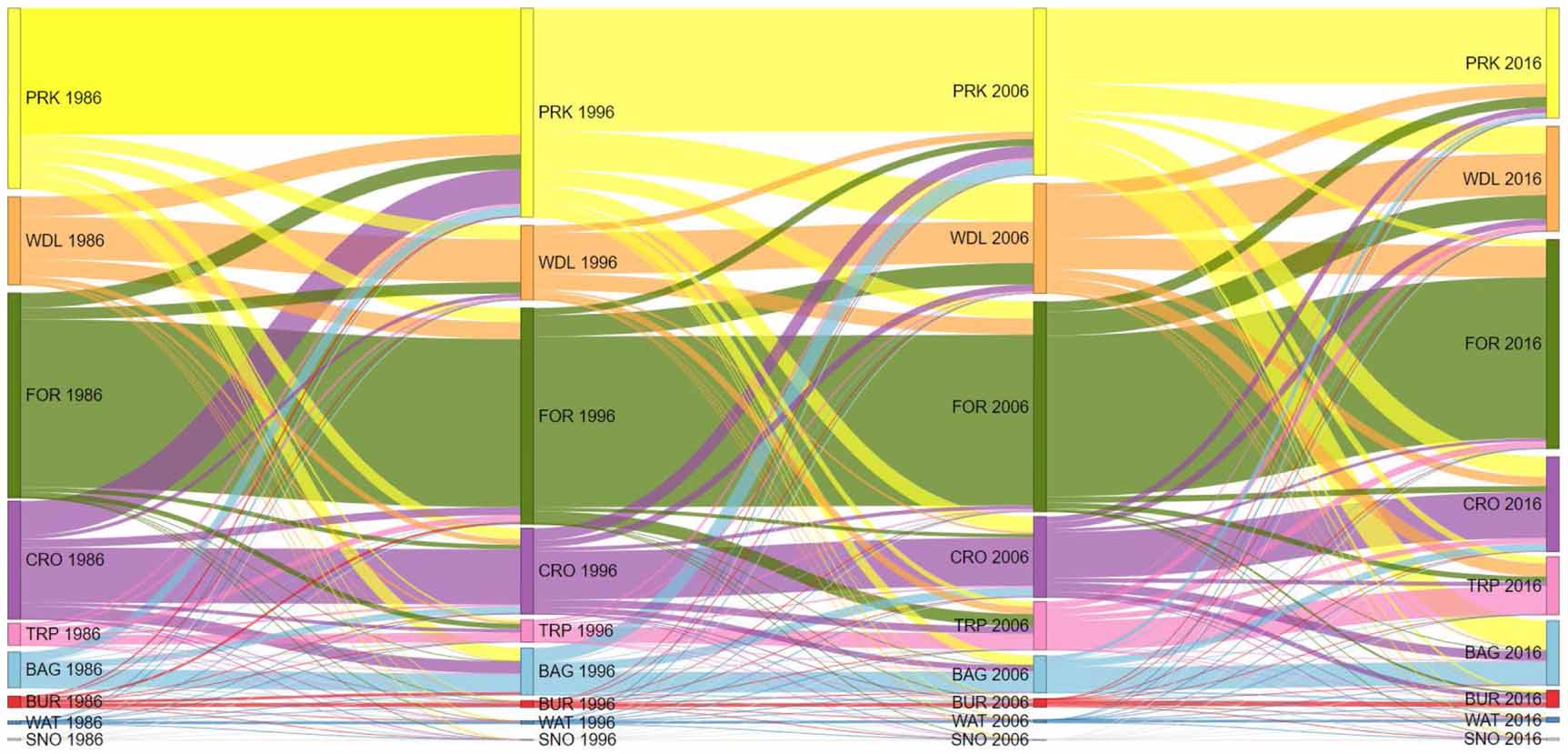 Sankey diagram of the land cover transitions in Yunnan Province, China from 1986 to 2016. Nodes indicate the land cover percentage for each particular time step, while the ribbons depict the transitions between land cover types. Colours follow that of the land cover map. Note: PRK: parkland, WDL: woodland, FOR: forest, CRO: cropland, TRP: tree plantations, BAG: bare ground, BUR: built-up area and bare rock, WAT: water bodies, SNO: snow.
Sankey diagram of the land cover transitions in Yunnan Province, China from 1986 to 2016. Nodes indicate the land cover percentage for each particular time step, while the ribbons depict the transitions between land cover types. Colours follow that of the land cover map. Note: PRK: parkland, WDL: woodland, FOR: forest, CRO: cropland, TRP: tree plantations, BAG: bare ground, BUR: built-up area and bare rock, WAT: water bodies, SNO: snow.
Abstract
Yunnan Province, southwest China, has a monsoonal climate suitable for a mix of fire-driven savannas and fire-averse forests as alternate stable states, and has vast areas with savanna physiognomy. Presently, savannas are only formally recognised in the dry valleys of the region, and a no-fire policy has been enforced nationwide since the 1980s. Misidentification of savannas as forests may have contributed to their low protection level and fire-suppression may be contributing to vegetation change towards forest states through woody encroachment. Here, we present an analysis of vegetation and land-use change in Yunnan for years 1986, 1996, 2006, and 2016 by classifying Landsat imagery using a hybrid of unsupervised and supervised classification. We assessed how much savanna area had changed over the 3 decades (area loss, fragmentation), and of this how much was due to direct human intervention versus vegetation transition. We also assessed how climate (mean annual temperature, aridity), landscape accessibility (slope, distance to roads), and fire had altered transition rates. Our classification yielded accuracy values of 77.89%, 82.16%, 94.93%, and 86.84% for our four maps, respectively. In 1986, savannas had the greatest area of any vegetation type in Yunnan at 40.30%, whereas forest cover was 30.78%. Savanna coverage declined across the decades mainly due to a drop in open parkland savannas, while forest cover remained stable. Savannas experienced greater fragmentation than forests. Savannas suffered direct loss of coverage to human uses and to woody encroachment. Savannas in more humid environments switched to denser vegetation at a higher rate. Fire slowed the rate of conversion away from savanna states and promoted conversion towards them. We identified remaining savannas in Yunnan that can be considered when drafting future protected areas. Our results can inform more inclusive policy-making that considers Yunnan’s forests and savannas as distinct vegetation types with different management needs.